This chapter demonstrates how to set up SIP trunking for PBX incapable of digest authentication so that:
- A call to one of the DIDs that the customer has purchased is processed by PortaSwitch and routed to the customer’s external PBX
- Outgoing calls from the customer’s PBX are processed and routed by PortaSwitch to carriers.
Please refer to the Cloud PBX (Hosted PBX) solution section for information on how to activate and use the PBX features available in PortaSwitch.
Checklist
Use this checklist to check off the operations you have completed while performing the system setup according to the instructions in this chapter. Please be sure to perform all of the operations in the order designated (all of the boxes should be checked), otherwise, the service will not work.
|
Operation |
Done |
|
Rating configuration (Vendor) |
|
|
Confirm that the DID supplier vendor and its “Calls from Vendor via SIP” connection has been configured according to the instructions in the Incoming calls from PSTN section |
|
|
Rating configuration (Vendor) |
|
|
Confirm that the internal vendor and its “Calls to vendor via SIP” connection has been configured according to the instructions in the PortaBilling initial configuration section. Check if the Internal connection use for field contains the “SIP-to-External SIP proxy (SIP-URI)” string for this vendor. Check if the tariff assigned has a zero cost rate for the wildcard destination (|). If you need to configure the internal vendor rating perform the following steps: Create a tariff (referred to as tariff A later on) that describes your termination costs for calls forwarded to SIP-URI (make sure it is NOT a Routing type!) |
|
|
Enter a zero cost rate for the wildcard destination (|) in tariff A |
|
|
Create an internal (virtual) vendor for keeping track of calls forwarded to SIP-URI (you can use the internal vendor created earlier) |
|
|
Create a “Calls to vendor via SIP” connection with the Remote gateway ID field containing the “SIP-URI” string for this vendor using tariff A |
|
|
Rating configuration (Customer) |
|
|
Create a tariff (referred to as tariff B later on) that will be used to calculate the charges for outgoing calls from customer’s PBX |
|
|
Enter rates in tariff B that cover the destinations where your customers can call |
|
|
Create a tariff (referred to as tariff C later on) that will be used to calculate the charges for incoming calls to DIDs |
|
|
Enter rates in tariff C that cover the DIDs you offer to your customers |
|
|
Create your SIP trunking product |
|
|
Create a rating entry for this product that associates the service Voice Calls and tariff B with the PortaSIP Node and OUTGOING Access code |
|
|
Create a rating entry for this product that associates the service Voice calls and tariff C with PortaSIP Node and INCOMING Access code |
|
|
Account provisioning |
|
|
Create a retail customer who will represent the PBX owner |
|
|
Create an account that will be used to authorize outgoing calls from PBX |
|
|
Create accounts for incoming DIDs (depending on PBX capabilities) |
|
|
Testing |
|
|
Provision the PBX to place outgoing calls via PortaSwitch |
|
|
Provision the PBX to receive incoming calls via PortaSwitch |
|
|
Check the parameters (SIP proxy address and port and optionally, account ID and password) in the BPX and then make a test call |
Initial configuration of PortaBilling
If you have just installed the PortaBilling software or dedicated a new billing environment to configure the services described in this handbook, make sure to first perform the initial configuration of PortaBilling and configure incoming calls from PSTN. To do this, use the PortaBilling initial configuration and Incoming calls from PSTN handbooks.
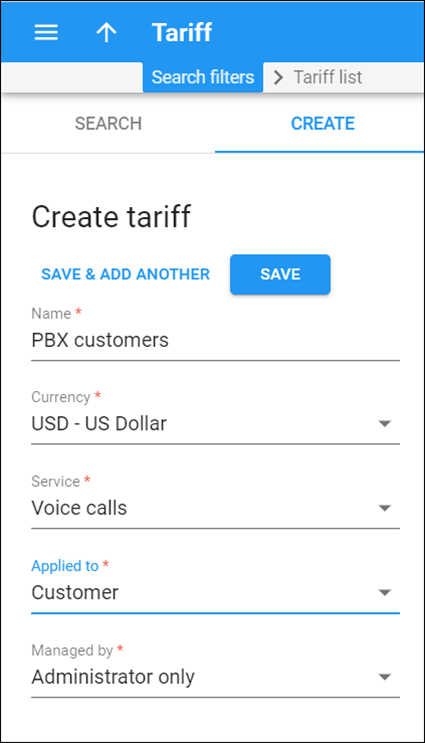
Create customer tariffs
You should create two separate tariffs for your PBX customer. These tariffs will be used for charging outgoing and incoming calls.
Follow the steps for creating customer tariffs below:
- On the navigation menu, select Service catalog and click Tariffs.
- On the Create tariff panel, fill in the tariff details:
- Name – a short name for the tariff object; this is the name you will see in the select menus.
- Currency – indicates in which currency pricing information is defined. All pricing information for a single tariff must be defined in the same currency.
The currency for the tariff is chosen only once, and cannot be changed later.- Service – select Voice calls.
- Applied to – select Customer as this tariff will be used to charge your customers.
- Managed by – select Administrator only here, since we are setting up a service without the involvement of resellers.
- Click Save.
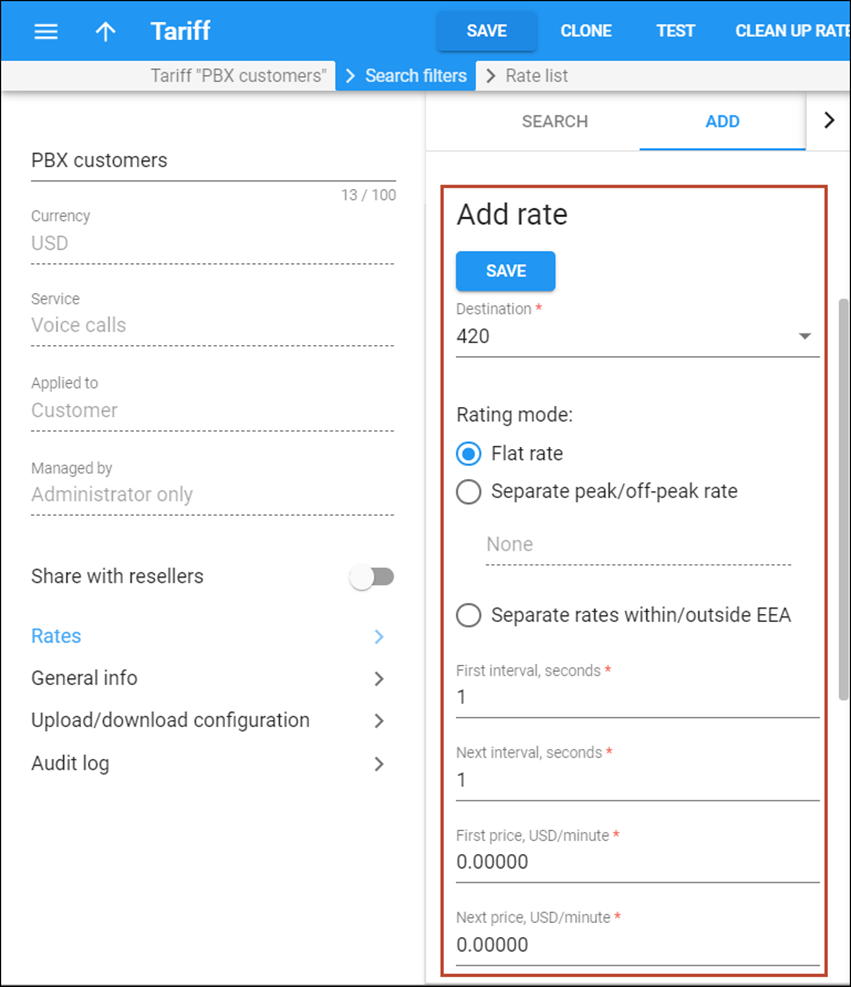
Enter rates
You should specify the rates for the two separate tariffs created in the previous section:
- Rates for the first tariff (referred to as tariff B in the checklist) should cover the destinations that your customers can call. They are used to calculate the charges for outgoing calls from the customer’s PBX.
- Rates for the second tariff (referred to as tariff C in the checklist) should cover the DIDs that the customer has purchased.
If you charge the same rate for forwarded calls as you do for outgoing calls and do not charge for calls made on your own network (a very typical case), you may use tariff B for both outgoing and forwarded calls.
 Rates can be
managed online and offline. Use the section below to add rates to all
tariffs.
Rates can be
managed online and offline. Use the section below to add rates to all
tariffs.
Managing rates online
- On the navigation menu, select Service catalog and click Tariffs.
- Use the Tariff search panel to locate the tariff you created. Specify one or more of the search criteria listed there and click Apply filters.
- On the Results panel, click your customer tariff name, which is also a link that redirects you to the edit tariff panel.
- On your customer tariff’s panel, click Rates.
- On the Add rate panel, fill in the rate details:
- Destination – select a destination prefix from the list or type it directly, e.g., 420 for Czech Republic.
You must create an entry for certain phone prefixes in the Destination register before creating a rate for them in the tariff.
- Rating mode – select the Flat rate option here. If you want to enter different rates for the peak and off-peak periods, select the Separate peak/off-peak rate option.
- First interval, seconds – type a first billing unit in seconds.
- Next interval, seconds – type the next billing unit in seconds.
- First price – type a per minute price for the first interval.
- Next price – type a per minute price for the next interval
- Off-peak first interval – type a first billing unit in seconds for off‑peak time.
- Off-peak next interval – next billing unit in seconds for off‑peak time.
- Off-peak first price – type a per minute price for first interval for off‑peak time.
- Off-peak next price – type a per minute price for next interval for off-peak time.
Off-peak fields appear only if the Separate peak/off-peak rate rating mode is selected or an off-peak period has already been assigned to this tariff on the General info panel.
- Rate formula – type a custom rating formula.
- Effective from – if you want this rate to take effect sometime in the future, you can either type in a date manually, or use the calendar (click on the DD-MM-YYYY link).
When using the calendar, you can specify that the date you are entering is in a different time zone than your present one. PortaBilling will then automatically adjust the time.
- Destination – select a destination prefix from the list or type it directly, e.g., 420 for Czech Republic.
- Click Save.
- Repeat these steps to enter more rates.
Managing rates offline
You also can upload rates from a file in .csv, .xls or .xlsx format – please consult the Rate import handbook for more details.
Repeat the Create tariff and Enter rates steps to create tariffs that can be used for charging customers for incoming calls.
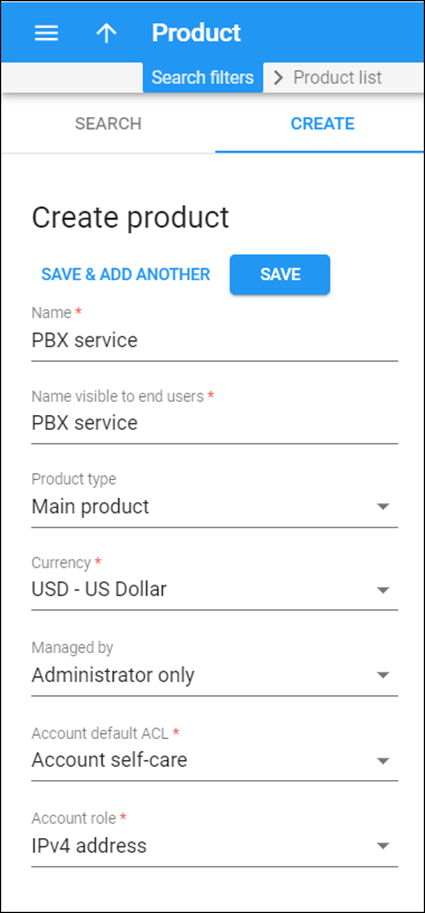
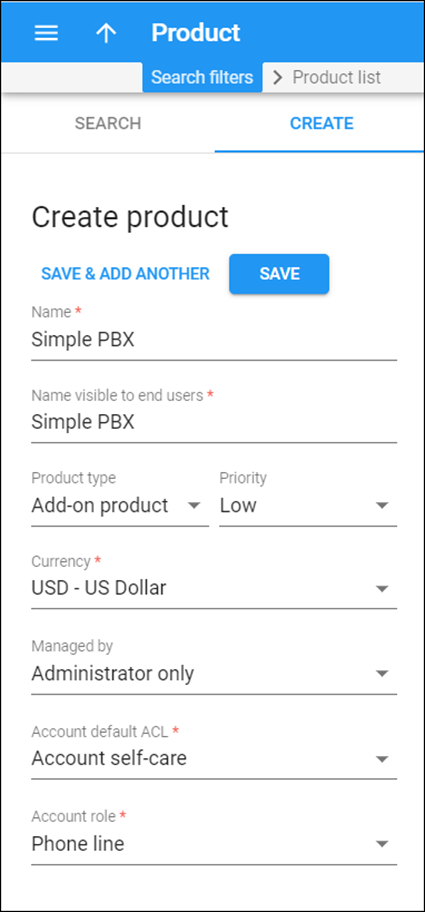
Create a product
Create a SIP trunking product.
- On the navigation menu, select Service catalog and click Products.
- On the Create product panel, fill in the product details:
- Name – type in a short name for the product; this is the name you will then see in the select menus.
- Name visible to end users – specify the name of this product that your customers will see on their self-care interface.
- Product type – select Main product here.
- Currency – choose a currency the product will be priced in.
- Managed by – select Administrator only here, since we are setting up a service without the involvement of resellers.
- Account default ACL – choose an Access Control List (ACL) for accounts with this product assigned. ACLs control which objects end users can access to and which actions they can perform.
- Account role – select IPv4 address from the list.
- Click Save.
Included services
Define which service types are included in the product. A service type is a description of the physical service provided to end users.
To add a service type:
- On your product’s panel, click Services.
- On the Services panel, click Add a service.
- In the Select services to add dialog box, select Voice calls and click Add.
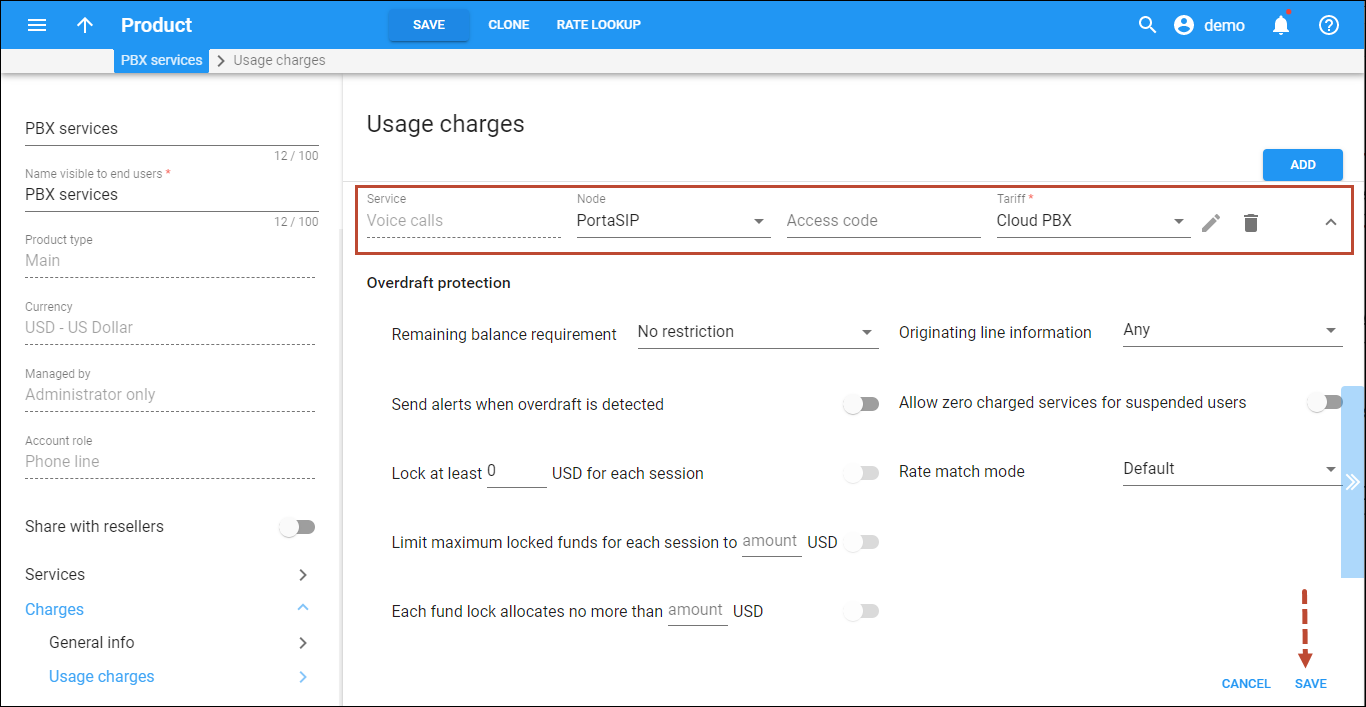
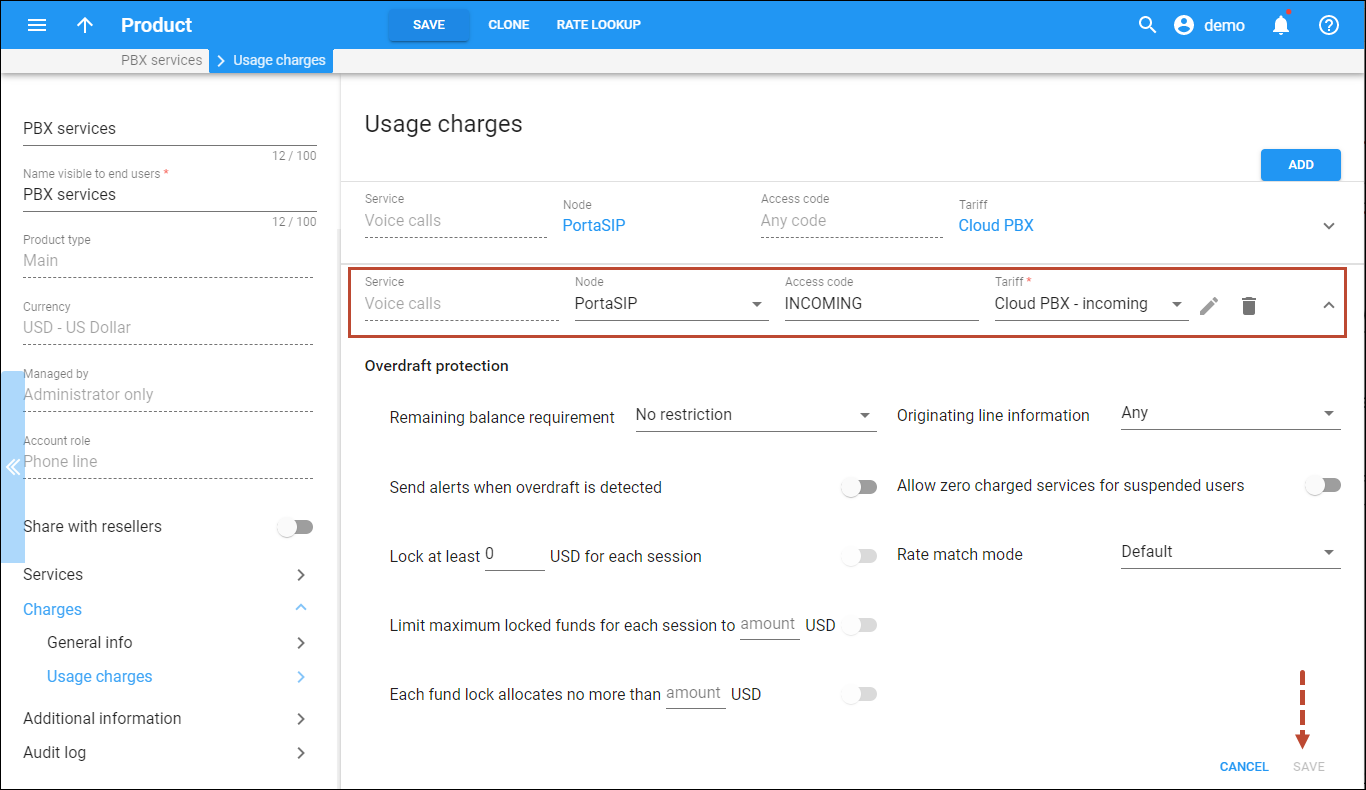
Create rating entries for the SIP trunking product
- On your product’s panel, click Charges, then click Usage charges.
- On the Usage charges panel, click Add.
- Fill in the required information:
- Service – select Voice calls.
- Node – select the PortaSIP node.
- Access code – leave this field empty for the basic SIP service.
- Tariff – select the tariff that will be used to calculate the charges for outgoing calls (referred to as tariff B in the checklist).
- Overdraft protection – to configure overdraft protection for this product, consult the Configure overdraft protection section within the product section in the Overdraft protection configuration handbook.
- Click Save.
- On the Usage charges panel, click Add to add the second rating entry.
- Fill in the required information:
- Service – select Voice сalls.
- Node – select the PortaSIP node.
- Access code – type INCOMING in this field.
- Tariff – select the tariff that will be used to calculate the charges for incoming calls (referred to as tariff C in the checklist).
- Overdraft protection – to configure overdraft protection for this product, consult the Configure overdraft protection section within the product section in the Overdraft protection configuration handbook.
- Click Save.
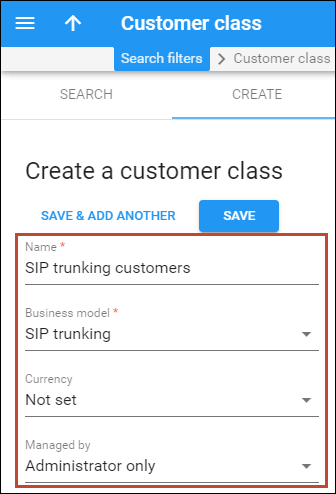
Create a customer class
Customer class provides the ability to define a business model and a group of parameters in a centralized way, and then apply those parameters to many customers at once.
- On the navigation menu, select Sales, then select Customer classes.
- On the Create a customer class panel, fill in the customer class details:
- Name – type a short name for this customer class.
- Currency – specify in which currency you charge the customers of this customer class. When specified, this customer class can only be assigned to customers with the same currency. Note that you can define the currency only when you create the customer class and can’t change it later.
- Business model – select which customers this customer class will apply. Select SIP trunking from the list.
- Description – type your comments about the intended use of this customer class.
- Click Save.
Follow the steps described in the Create a customer class section of the Basic residential VoIP service handbook and to configure the customer class.
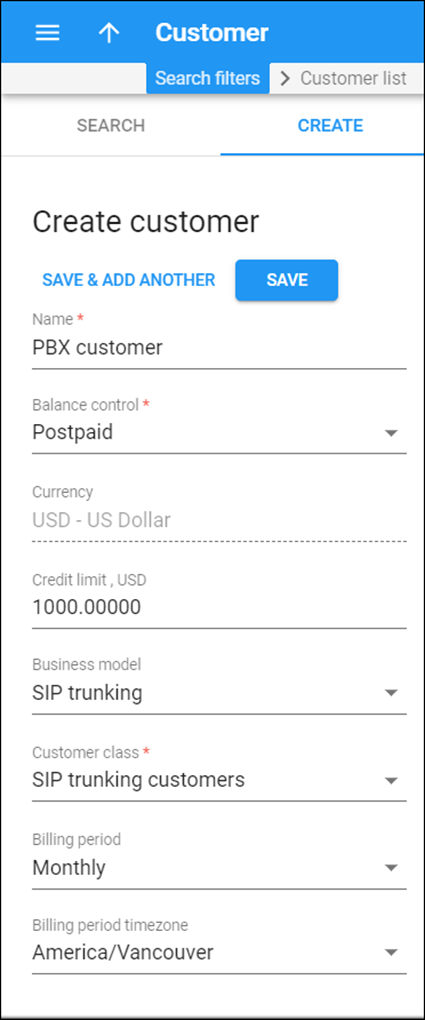
Create a customer
- On the navigation menu, select Sales, then select Customers.
- On the Create customer panel, fill in the customer details:
- Name – type a short name for the customer object; this will be used on the web interface.
- Balance control – specify the way the customer will pay for the service: Postpaid – after consuming the services; Prepaid – prior to consuming the services. Select Postpaid in this field.
- Currency – choose the currency in which this customer will be billed.
- Credit limit – assign a credit limit for the customer.
- Business model – a business model defines what type of service is to be provided to the customer. Select SIP trunking for this customer.
- Customer class – customer class allows you to define a policy for automated payment collection. By choosing a specific class here the customer will automatically inherit all of the class properties (grace period, invoice template, etc.). Select the previously created customer class.
- Billing period – choose a billing period for the customer. A billing period defines the frequency of invoicing for this customer.
- Billing period time zone – choose a time zone in which customer’s billing period will be closed and invoices will be generated.
- Click Save.
Personal info
Define the customer’s personal information (such as name, email address, and etc.).
- On your customer’s panel, click Personal, then click General info.
- On the General info panel, fill in the customer’s personal information and an email address for the receipt of accounting information. After the billing period is over, a list of xDRs and other statistics will be sent to this address.
Web self-care
Define credentials and preferred settings (such as language, time zone, date input and output formats) for this customer’s self-care interface.
- On your customer’s panel, click Personal, click General info, then click Web self-care.
- On the Web self-care panel, define credentials for the customer self-care interface (such as login, password, time zone, etc.) and other preferred settings.
Credit limit
- On your customer’s panel, click Finances, click General info, then click Credit limit.
- On the Credit limit panel, define the Credit limit warning threshold
parameter. The customer can be notified by email when his balance is dangerously
close to the credit limit and service will soon be blocked. The threshold can be specified:
- As a percentage (e.g., 90%). The warning will be sent when the customer’s balance exceeds that percentage of his credit limit. So, if the credit limit is USD 1000.00 and the threshold is 90%, a warning will be sent as soon as the balance exceeds USD 900.00. This is only applicable when the customer has a positive credit limit.
- As an absolute value. The warning will be sent as soon as the balance goes above the specified value.
Invoices and taxation
Define whether to send this customer their statistics and invoices by email.
- On your customer’s panel, click Finances, and then click Invoices and taxation.
- On the Invoices and taxation panel, set the Send Statistics via email option to Summary only. This delivers a call summary only and do not attach a details file; this could be useful in the case of a large number of calls. Other options are Full Statistics (attach a complete list of xDRs) or Do not send (this option prevents the delivery of event statistics to this customer via email).
Services
- On your customer’s panel, click Services.
The Services panel provides an access to a group of panels where you can activate/deactivate various features of the voice calls service provided to the customer.
This is a convenient way for managing parameters which are the same for a whole set of accounts. Instead of trying to configure them for each individual account, you can define them once at the customer level, then specify in the account configuration that the value in the customer’s configuration be used. Should you wish to change this value later, you need only modify it once for the change to be automatically propagated to all accounts.
Click
 Help for a description
of parameters available here. For now, you may leave these with their
default values. If you change them later, these changes will automatically
affect all accounts created under this customer.
Help for a description
of parameters available here. For now, you may leave these with their
default values. If you change them later, these changes will automatically
affect all accounts created under this customer. - Click Save.
Create accounts
Please refer to the Create accounts section of the Basic residential VoIP service handbook for the general steps of account creation. The steps below help you configure accounts depending on the PBX features and preferences.
Accounts for outgoing calls from PBX
For PBX incapable of digest authentication, you should implement IP-based authentication to allow establishing outgoing calls.
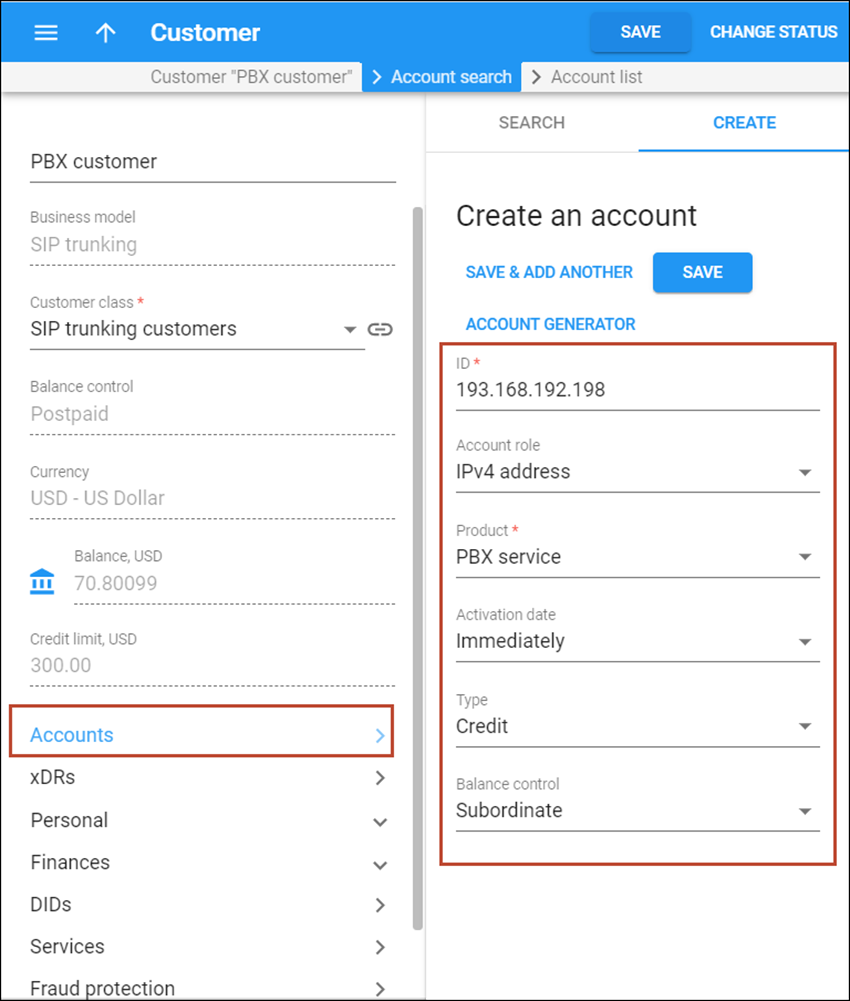
Thus, create an account with the following options:
- On your customer’s panel, click Accounts.
- On the Create an account panel, fill in the account information:
- ID – the IP address of the customer’s PBX server.
- Account role – select IPv4 address from the list.
- Product – choose the main product, which you would like your account to have.
- Activation date – choose the date from which the account is usable. By default, the account is activated immediately upon creation.
- Type – select Credit in this field.
- Balance control – define the way the balance of the account is controlled. Subordinate – the balance will directly depend on the customer’s balance (only the customer tops up the balance); Individual credit limit – this account may have its own balance and credit limit (the customer credit limit still applies.) Select Subordinate in this field.
- Click Save.
Accounts for incoming calls to PBX
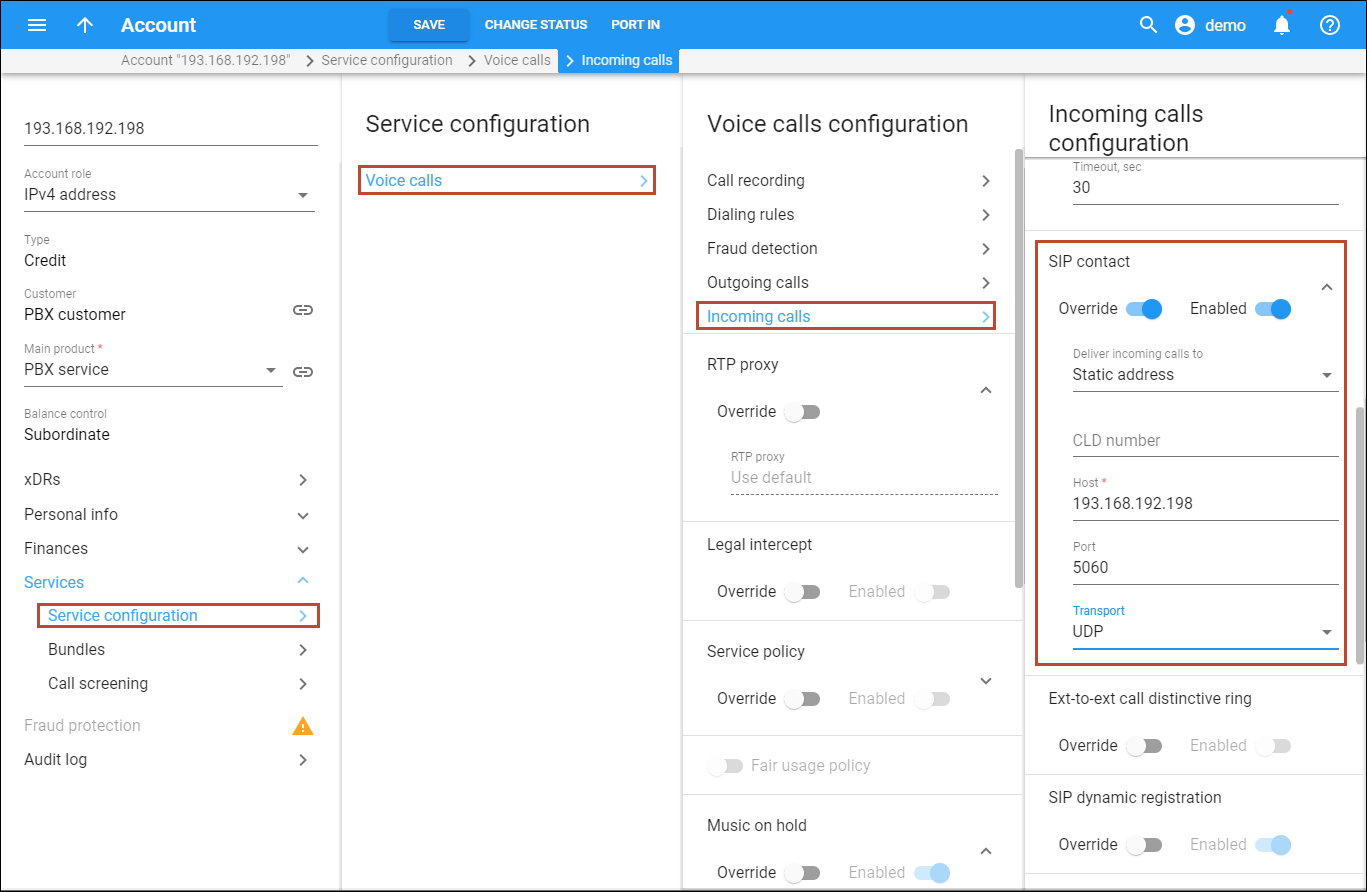
Method 1. Enable SIP Contact for the main PBX account
The “SIP Contact” functionality has the ability to imitate the registration of a PBX (by supplying its IP address and port), so any call to a DID is delivered to the PBX as a “normal” incoming call.
To enable SIP contact, do the following:
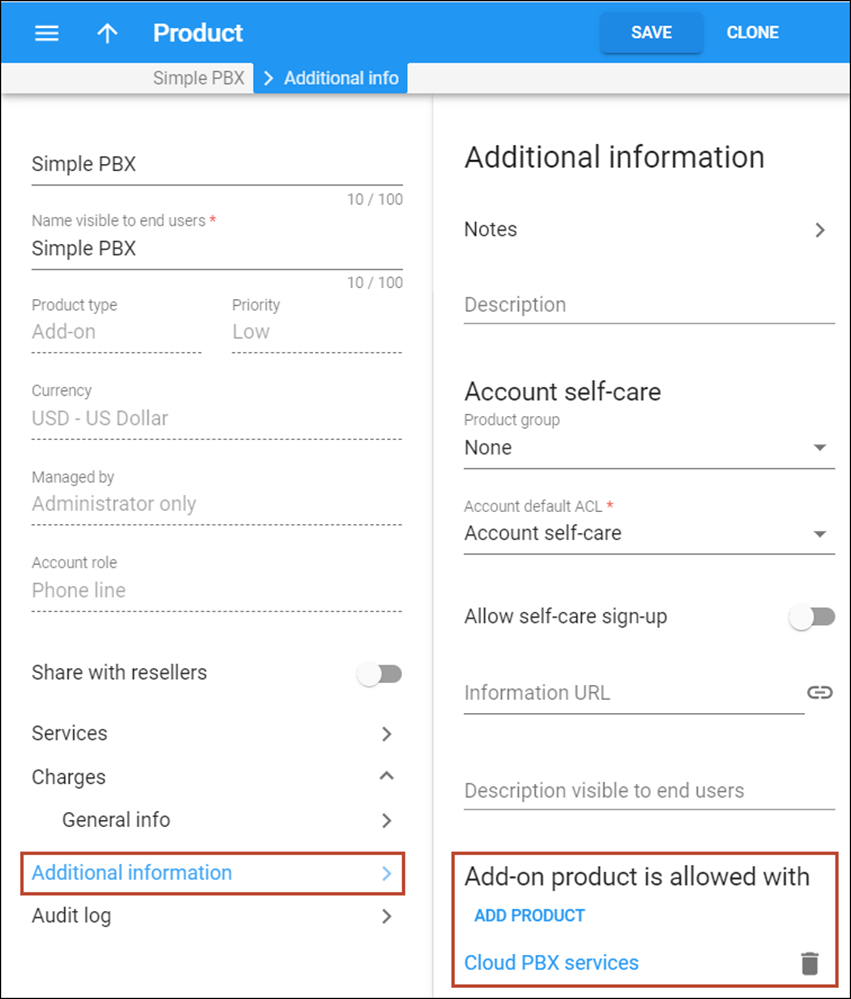
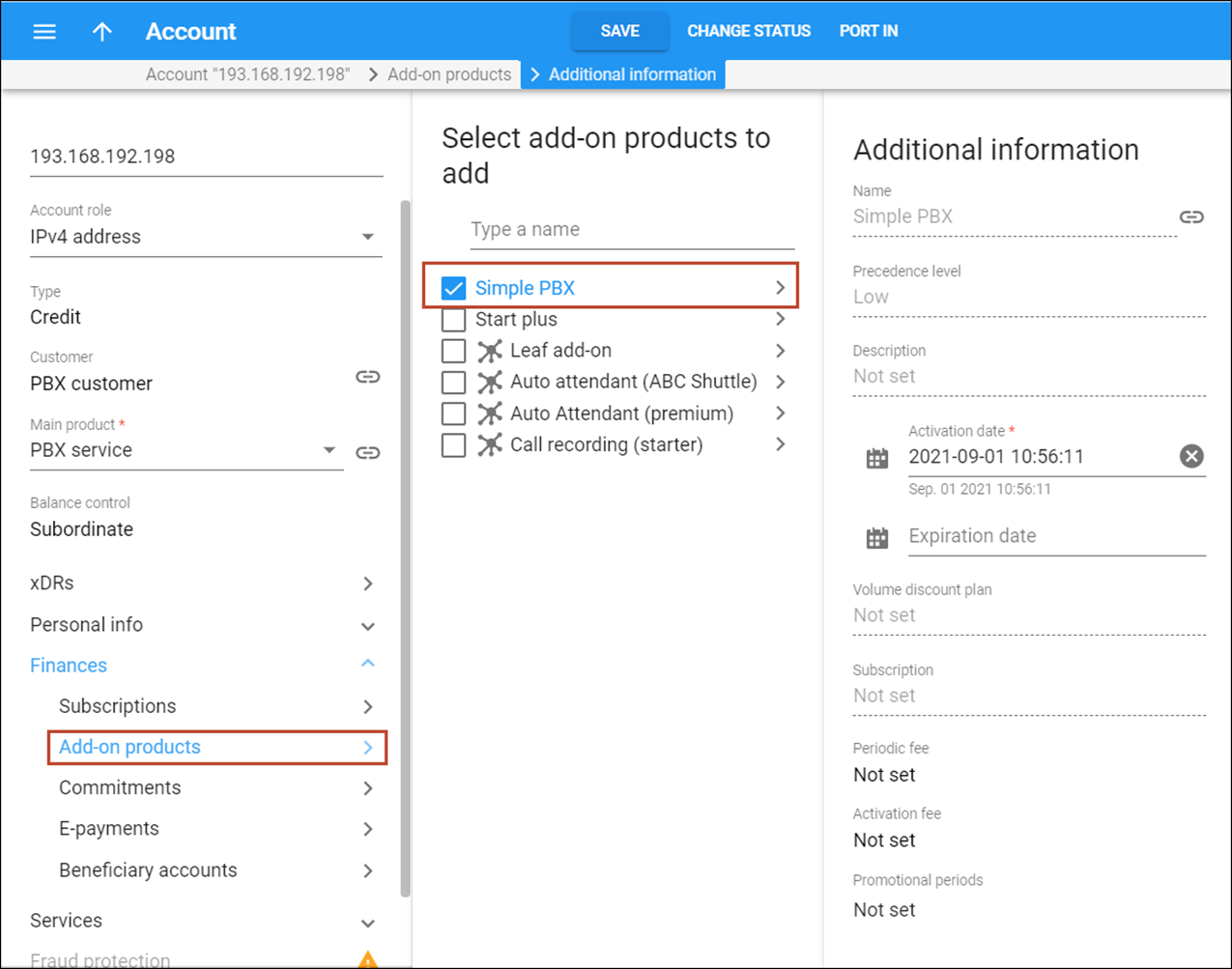
- Create an add-on product and specify the account role as Phone line within.
- Create an account for this customer as described in the Create accounts section (Account ID is the IP address of the customer’s PBX server) and assign the add-on product to this account.
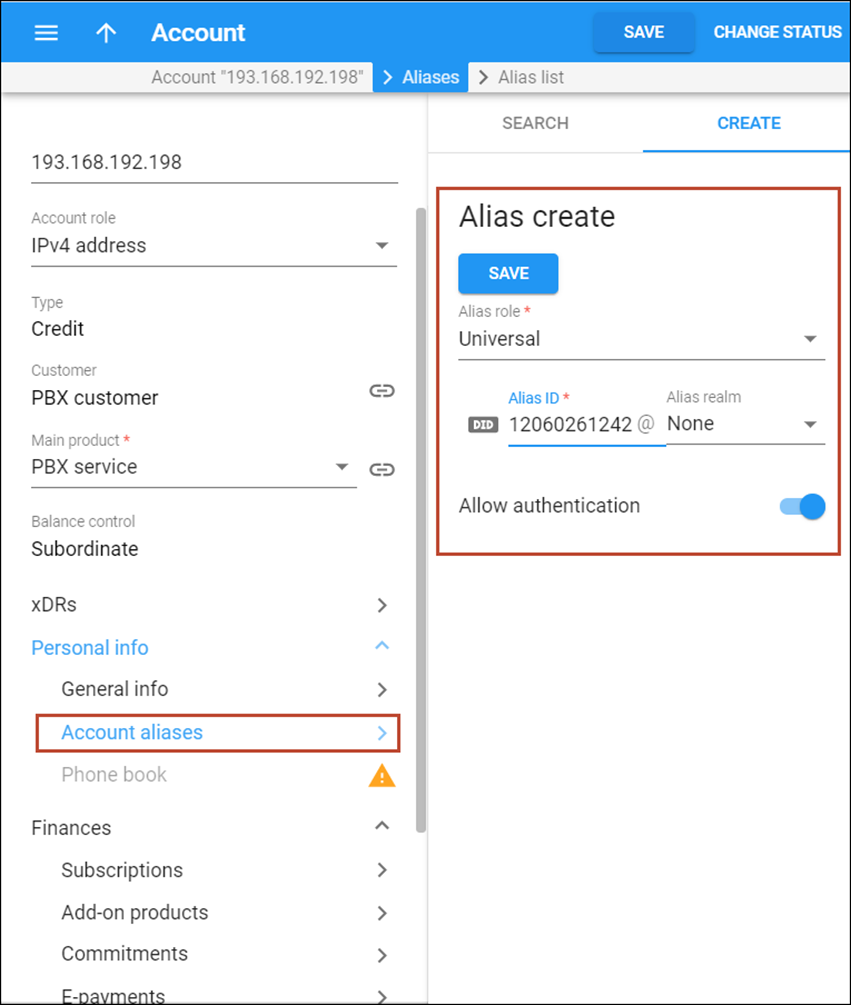
- Go to the Aliases tab and add a DID number as an alias. Please refer to the …create extra DIDs as aliases? chapter in the How to… section for detailed description.
- On the Account page, click Services and select Service configuration.
- On the Service configuration panel, select Voice calls, click
on the Incoming calls link and follow the steps below to enable SIP contact:
- Use a slider to enable the SIP Contact option.
- In the Deliver incoming calls to field select the Static address option.
- In the Host field, enter the IP address of the PBX.
- In the Port field, enter the PBX port for SIP communication to which requests are sent (5060 port is used by default).
- In the Transport field, select the transport protocol that will be used for SIP communication.
- Click Save.
This functionality simplifies the configuration of SIP trunking services and the intuitive xDR presentation enhances the user experience, thus decreasing the support assistance required by end-users. This also permits your customers to use PBX features that are dedicated to incoming calls and use forwarding or voicemail if the call fails.
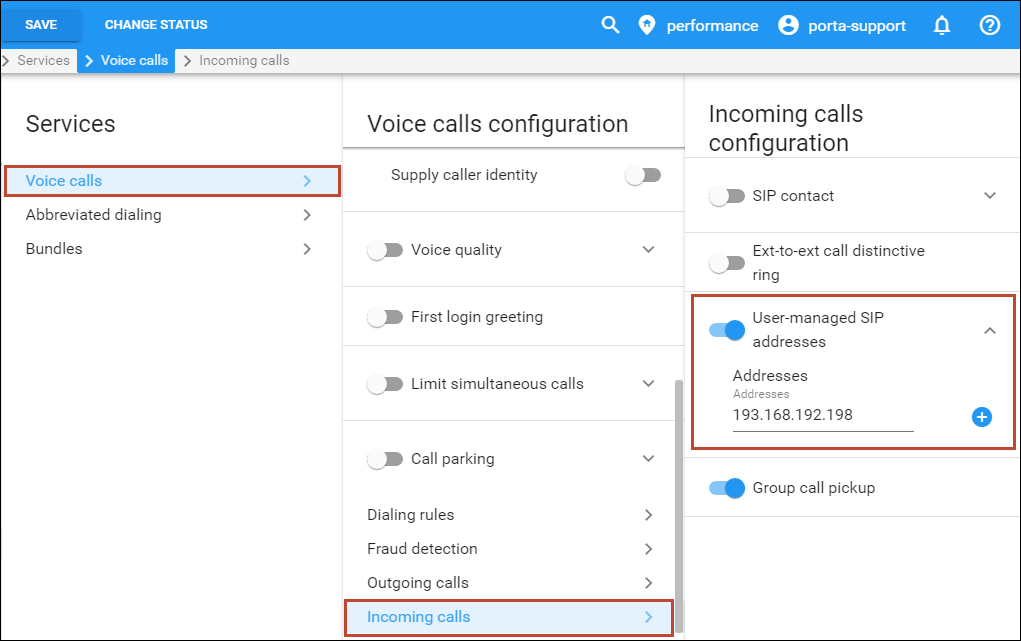
Method 2. Forwarding to SIP URI
- Specify the PBX IP addresses where you will forward incoming calls for the customer.
- Click
 to
return to the Edit customer page, click Services, select Voice
calls and click on Incoming calls.
to
return to the Edit customer page, click Services, select Voice
calls and click on Incoming calls. - Enable the User-managed SIP addresses option and specify the IP addresses where you will forward incoming calls for the customer.
- Click Save.
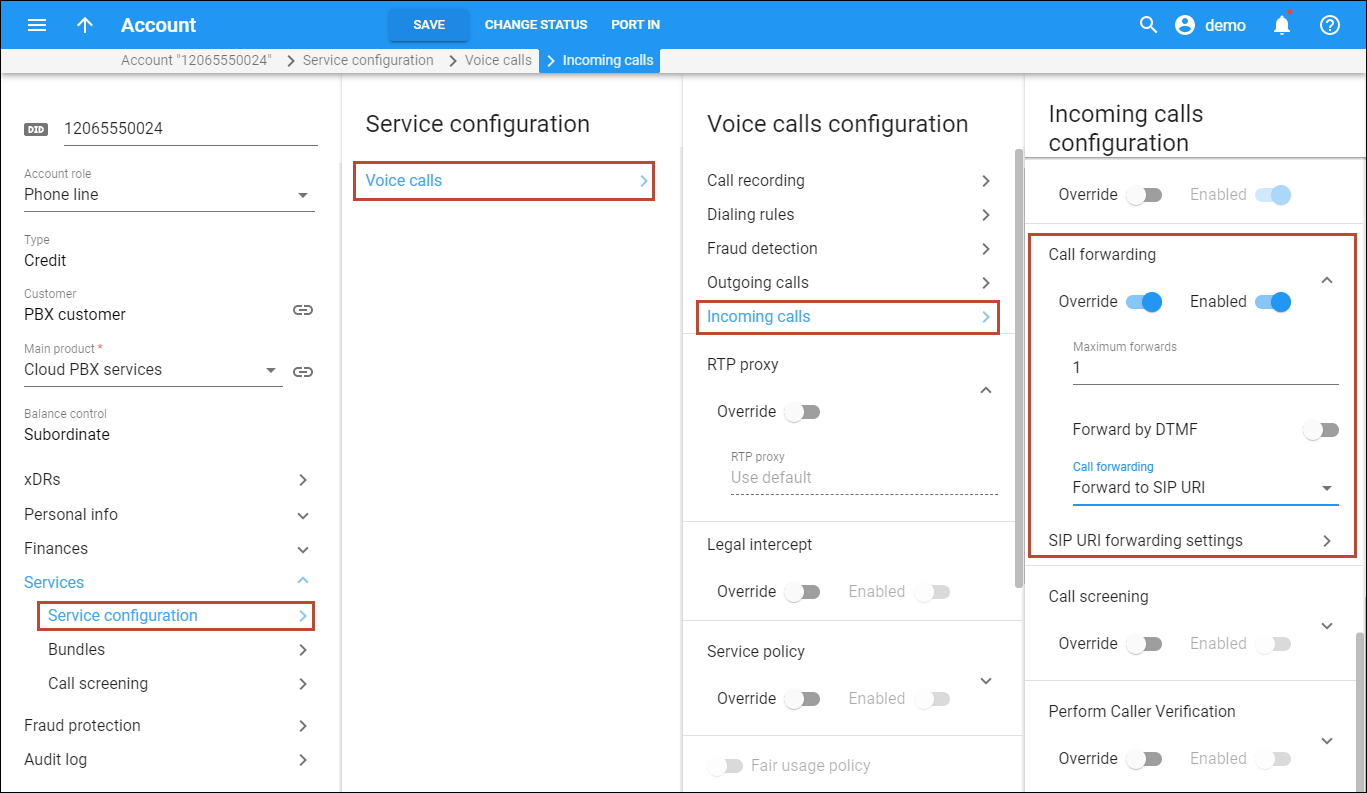
- Create a main SIP trunking product with a phone line account role and create a rating entry for it for incoming calls (Follow the steps described above in the Create a product section of this handbook).
- Create an account for this customer as described in the Create accounts section of the Basic residential VoIP service handbook (Account ID is a DID number used for forwarding calls to an external PBX).
- Go to the account’s Service configuration page, select Voice calls and click on the Incoming calls link:
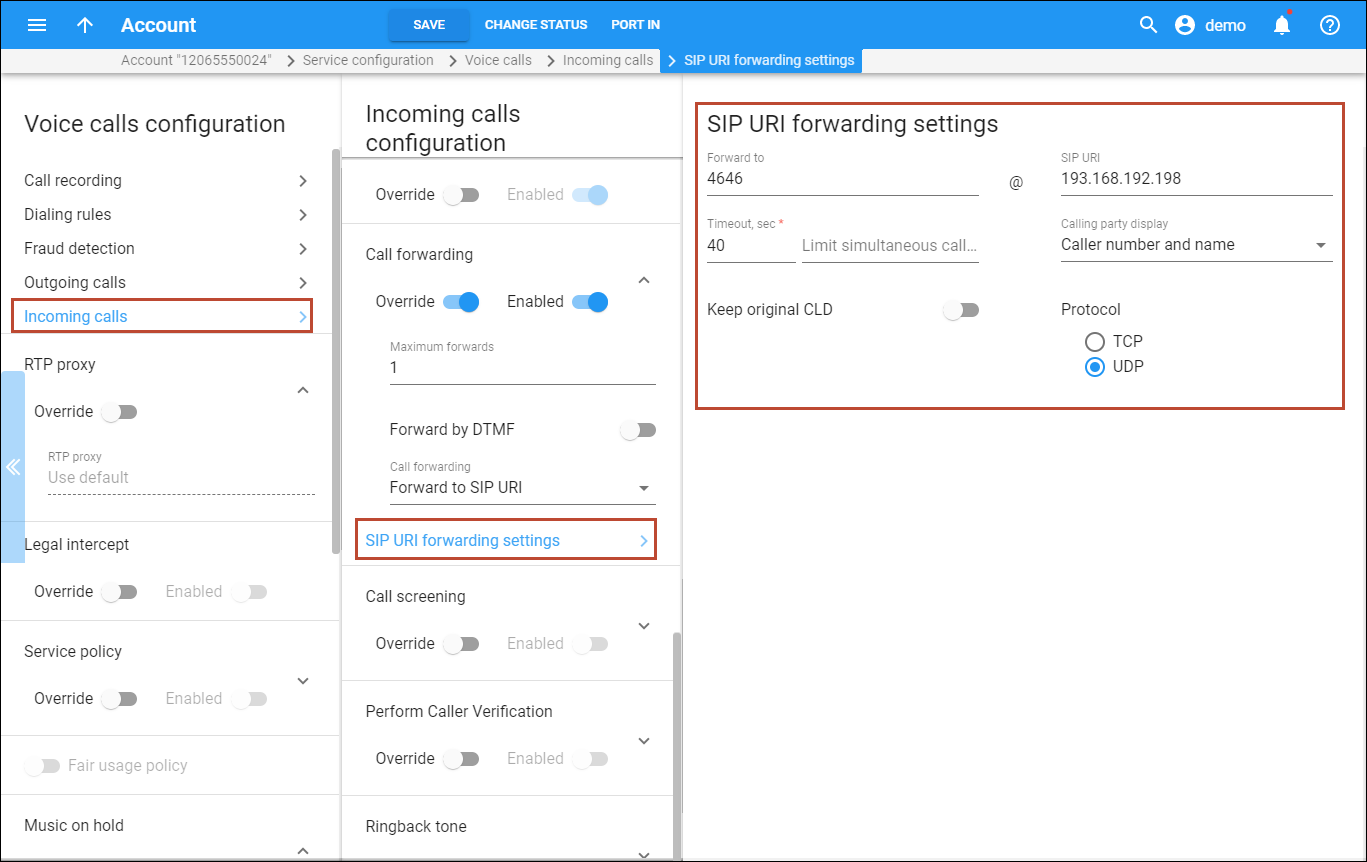
- Go to the SIP URI forwarding settings panel:
- Specify an appropriate CLD and IP address for your PBX in the Forward
to and SIP URI fields.
SIP URI values should contain one of the following: IP, IP:port, domain or domain:port. So, if your PBX uses a port different from 5060 for incoming calls, you should specify that port here.
- Activate the Keep original CLD option to store the original DID. The PBX can then correctly route these calls to extensions. (Please consult the Forwarding with the original DNIS (CLD) section for a detailed description).
- Click
 Help
for a description of parameters available here. For now, you may leave
these default values.
Help
for a description of parameters available here. For now, you may leave
these default values. - Click Save.
- Repeat these steps if you need to create additional accounts for forwarding calls to PBX.