Mobile Virtual Network Operators (MVNOs) typically depend on their host Mobile Network Operators (MNOs) to set an internet speed limit for users. This reliance can restrict their ability to launch new products with specific bandwidth needs. For example, if an MVNO wants to offer an unlimited data package, they must implement a fair usage policy to reduce speeds for users who exceed a specific limit, like 30 GB, to avoid network overuse.
With this release, MVNOs can use a netElastic virtual Broadband Network Gateway (vBNG), a software-based gateway that manages internet services, to gain more flexibility and control over bandwidth settings, without the need to contact the MNO. In this scenario, internet traffic of MVNO subscribers flows from the MNO’s network through vBNG, where Quality of Service (QoS) profiles with different bandwidth limits are configured. PortaBilling authenticates and authorizes user sessions on the MNO’s network and informs the vBNG which QoS profile (such as “Uncapped_LTE_regular” or “Uncapped_LTE_limited”) should be applied to this user session, depending on whether the user has exceeded the defined quota (e.g., 30 GB).
To provide data service, the MVNO “Owl Mobile” relies on the LTE network infrastructure of the host MNO, which provides a standard bandwidth of 100 Mbps. The MVNO is planning to introduce a new data plan: “Unlimited wireless data for $39.99 per month.” The MVNO’s Fair Usage Policy states that the speed should be reduced to 1 Mbps once usage reaches 30 GB.To achieve this, the MVNO implements a vBNG, integrating it with their PortaBilling system. On the vBNG, the MVNO creates the following QoS profiles:
- “Uncapped_LTE_regular” (sets bandwidth to 100 Mbps)
- “Uncapped_LTE_limited” (sets bandwidth to 1 Mbps)
Once customer John Doe signs up for the "Unlimited wireless data for $39.99 per month" plan on September 1st and initiates an internet connection, PortaBilling verifies that his available quota is 30 GB and instructs the vBNG to apply the QoS profile “Uncapped_LTE_regular,” allowing John to enjoy high-speed internet. After two weeks of usage, John reaches the 30 GB threshold. While his current session remains active, PortaBilling instructs the vBNG to switch to the QoS profile “Uncapped_LTE_limited.” John continues browsing, but his internet speed is now throttled to 1 Mbps.
MVNOs can create competitive internet packages without being limited by MNO.
How it works
When a customer uses the internet service, the process is as follows:
- A user initiates an internet session.
- PortaBilling authenticates the user and authorizes the internet session in the mobile network.
- PortaBilling sends a RADIUS Change of Authorization (CoA) request to BNG.
In a CoA request, PortaBilling sends the following parameters:
- NetElastic-Qos-Profile-Name – consists of the “Package name” value specified in the service policy assigned to an account and automatically added access status (“regular,” “limited”, or “blocked”) in the format: <Package_name>_<Access_Status>, e.g., “Uncapped_LTE_regular.”
The NetElastic-Qos-Profile-Name value should correspond to the name of a QoS profile configured on the vBNG.
For example, if a user is authorized and PortaBilling verifies that they have enough quota, PortaBilling sends a CoA request with the “regular status” (the “Uncapped_LTE_regular” profile). Once a user reaches their data quota, PortaBilling sends a CoA request with the “limited” status (the “Uncapped_LTE_limited” profile) to the vBNG, reducing the internet bandwidth for this session. And when a session is disconnected, PortaBilling sends a CoA request with the "blocked" status (the “Uncapped_LTE_blocked” profile).
- Framed-IP-Address – the IP address of the user session present in the request received from the MNO network.
- User-Name – the account’s MSISDN (mobile number).
- NetElastic-Qos-Profile-Name – consists of the “Package name” value specified in the service policy assigned to an account and automatically added access status (“regular,” “limited”, or “blocked”) in the format: <Package_name>_<Access_Status>, e.g., “Uncapped_LTE_regular.”
The vBNG applies the bandwidth based on the QoS profile specified in the CoA request.
Configuration
Before configuring the integration with the netElastic vBNG, set up the vBNG. For example, configure the QoS profiles on the vBNG:
- A profile for regular bandwidth (e.g., 100 Mbps), named <Package_name>_regular (e.g., "Uncapped_LTE_regular").
- A profile for limited bandwidth (e.g., 1 Mbps), named <Package_name>_limited (e.g., "Uncapped_LTE_limited").
- A profile to be used when the service should be blocked, named <Package_name>_blocked (e.g., "Uncapped_LTE_blocked").
To set up the bandwidth control via the netElastic vBNG:
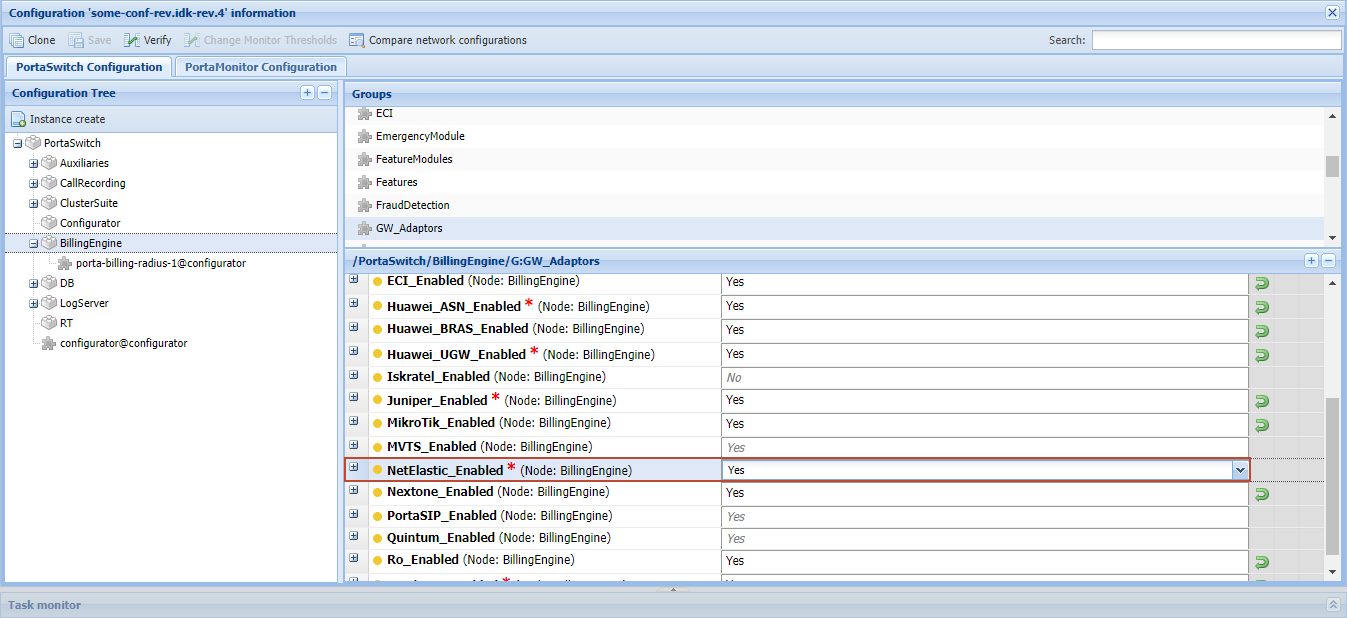
- Enable the dedicated netElastic module on the Configuration server web interface by setting the NetElastic_Enabled option to Yes.
- On the PortaBilling web interface, add vBNG as a node for sending CoA requests:
- Navigate to Infrastructure > Nodes
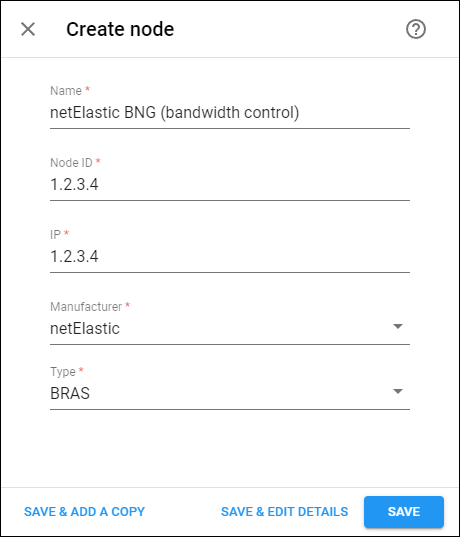
- Click Add and fill in the node details:
- Name – a short descriptive name for this node
- Node ID – since the node will be identified by the IP address specified in the “POD Server” section, you can specify a “dummy” value here.
- IP – since the node will be identified by the IP address specified in the “POD Server” section, you can specify a “dummy” value here.
- Manufacturer – select netElastic.
- Type – select BRAS (Broadband Remote Access Server).
- In the node settings, turn on the Enable communication with billing toggle and fill in the details:
- Client protocol – select RADIUS.
- RADIUS key – specify the authentication key for the RADIUS interactions. Since this node will only be used as “POD server,” you can specify a dummy value here.
- RADIUS source IP – this field is populated automatically with the value you specified during the node creation.
- Configure the node as a “POD server":
- Turn on the POD server toggle.
- Shared key – specify the authentication key for authentication requests. Click Generate <icon> to generate a hard-to-guess key. Note that this field is automatically populated with the “RADIUS key” value.
- Radius IP – specify the IP address of your vBNG where the CoA requests will be sent.
- Port – specify the port.
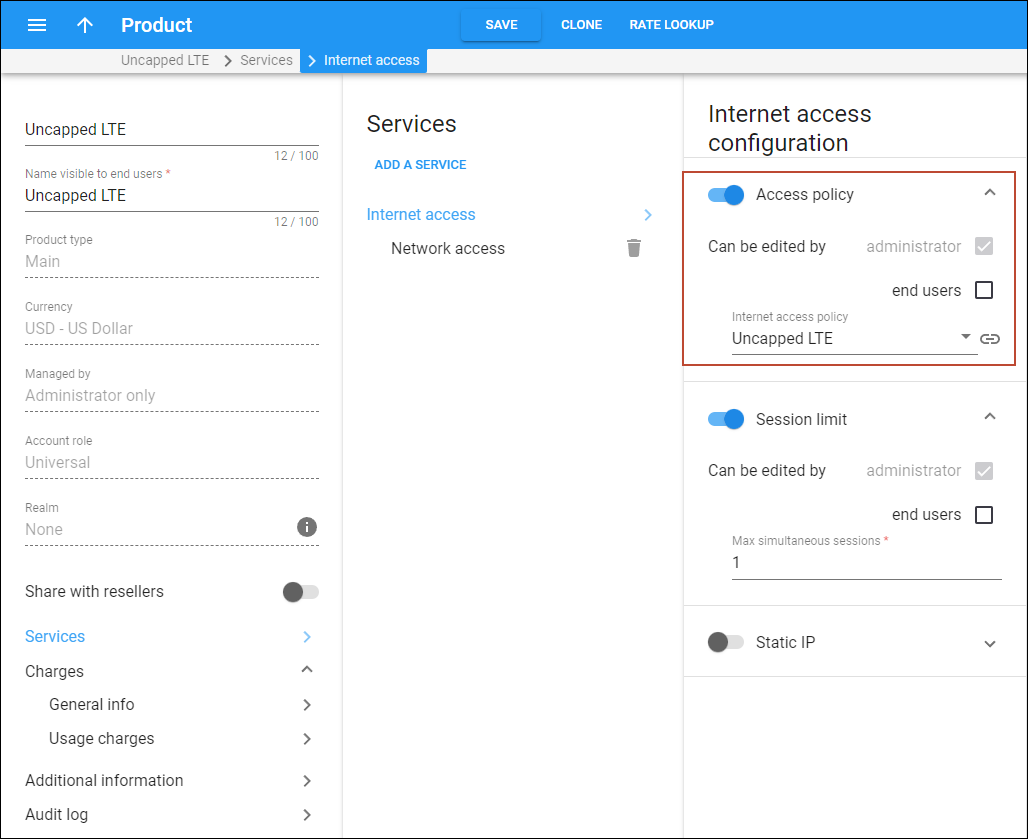
- Set up a service policy:
- Assign the created service policy to the product (or a specific account).